Understanding How Solar Panel Farms Operate
Introduction to Solar Panel Farms
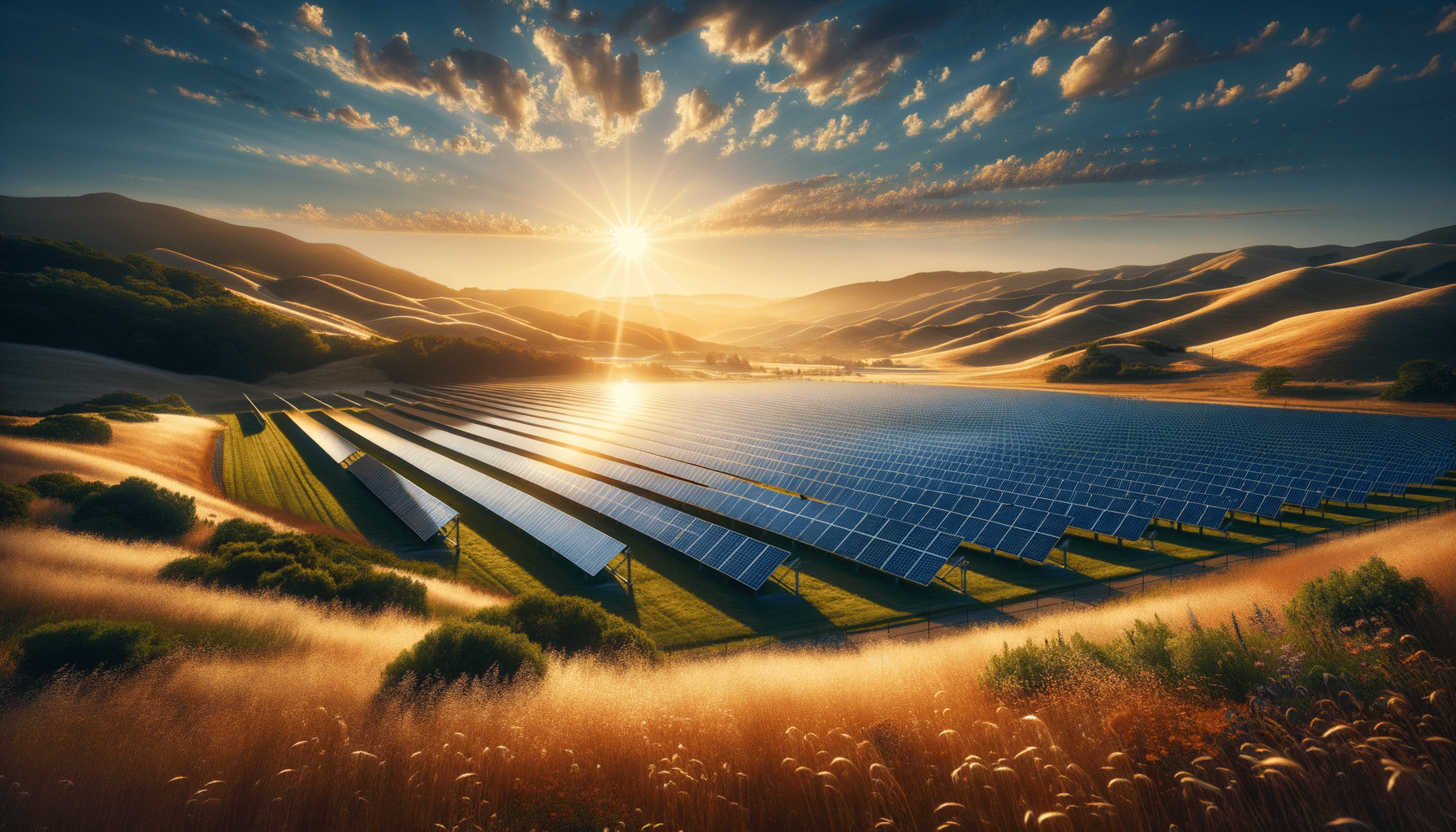
Solar panel farms, often referred to as solar parks or photovoltaic power stations, represent a transformative shift in the way we produce and consume energy. As the global community confronts the daunting challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, the pursuit of renewable energy solutions has never been more urgent. Solar panel farms stand at the forefront of this movement, offering a clean, sustainable means of generating electricity. These expansive installations are typically situated in regions blessed with abundant sunshine, optimizing their capacity to harness solar energy. By converting sunlight into electricity, solar panel farms play a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and mitigating the adverse effects of climate change.
The Mechanics of Solar Panel Farms
At the heart of a solar panel farm lie photovoltaic (PV) panels, which are meticulously arranged to capture the sun’s rays. These panels are composed of numerous solar cells made from semiconductor materials, most commonly silicon. When sunlight strikes these cells, it excites electrons, generating an electric current. This process, known as the photovoltaic effect, is the fundamental principle behind solar energy conversion. The electricity produced is direct current (DC), which must be converted to alternating current (AC) using inverters to be compatible with the power grid. Solar panel farms are equipped with a network of inverters and transformers, ensuring efficient energy conversion and distribution. This intricate setup allows solar farms to produce substantial amounts of electricity, sufficient to power thousands of homes and businesses.
Environmental and Economic Impact
The environmental benefits of solar panel farms are profound. By generating electricity without burning fossil fuels, these installations significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier planet. Furthermore, solar energy is renewable and inexhaustible, providing a sustainable alternative to finite resources like coal and oil. Beyond environmental advantages, solar panel farms offer compelling economic benefits. They create jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, fostering economic growth and stability. Additionally, by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels, solar farms enhance energy security and resilience. As technology advances and costs decline, solar energy becomes increasingly accessible, offering a viable path toward a more sustainable future.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite their numerous advantages, solar panel farms face several challenges. One primary concern is land use, as these installations require large tracts of land, which may lead to conflicts with agricultural or conservation interests. To address this, researchers are exploring innovative solutions such as agrivoltaics, where solar panels are integrated with agricultural activities, allowing for dual land use. Another challenge is energy storage, as solar power generation is intermittent and dependent on weather conditions. Advances in battery technology and grid management are crucial to overcoming this hurdle, ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply. Policy support and incentives also play a vital role in promoting the adoption of solar energy, helping to overcome financial and regulatory barriers.
The Future of Solar Panel Farms
As the world transitions toward a more sustainable energy paradigm, the future of solar panel farms looks promising. Technological innovations continue to enhance the efficiency and affordability of solar energy, paving the way for widespread adoption. Emerging trends such as floating solar farms and integrated solar systems offer new opportunities for harnessing solar power in diverse environments. Moreover, international cooperation and policy frameworks are crucial in scaling up solar energy deployment, fostering global collaboration to combat climate change. As solar panel farms become more prevalent, they will play an increasingly important role in shaping a cleaner, greener energy landscape, contributing to a sustainable and prosperous future for all.